
Developing a novel mobile phone app to promote Snacktivity™: the SnackApp
SnackApp is a new smartphone app designed to increase physical activity. User testing showed that the SnackApp was well received by participants and was used regularly during the study.
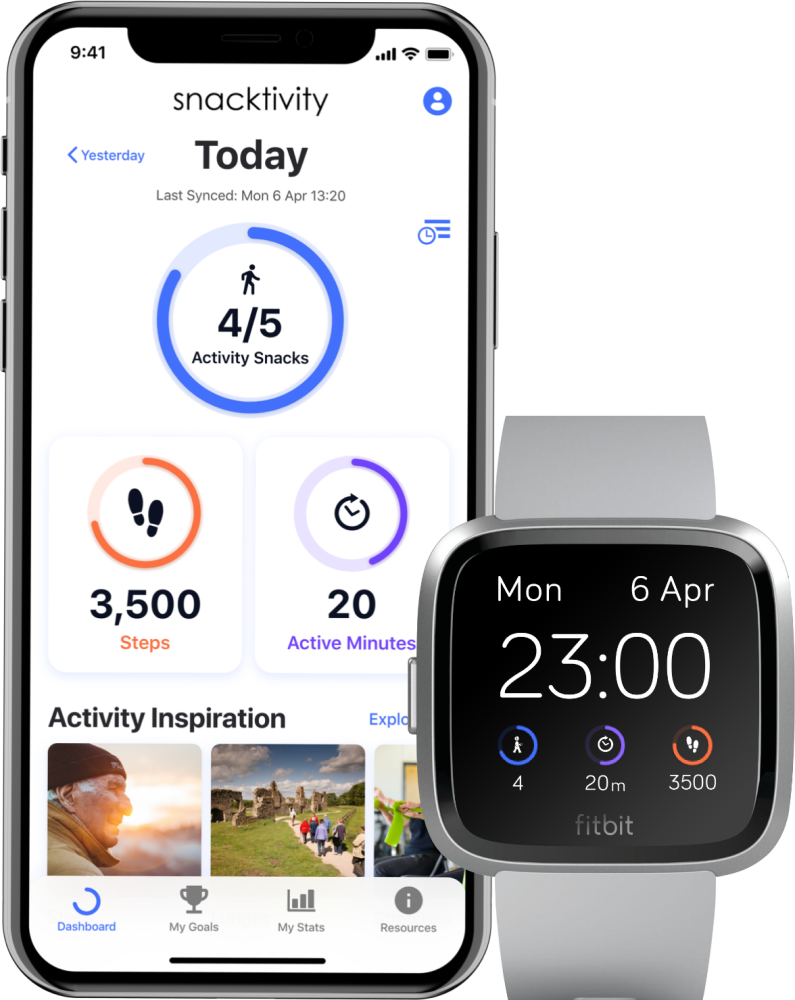
We used the intervention mapping framework to develop the SnackApp, a novel mobile app aimed at increasing short bouts of physical activity (Snacktivity™) in the general population. The SnackApp is a cross-platform app which links to the Fitbit Versa series smartwatches to help users track their physical activity by nudging them to incorporate Snacktivity™ throughout their daily lives.
Once developed, we conducted some user testing of the app in 15 inactive adults over four weeks. Participants engaged with the SnackApp an average of 77 times, spending approximately 13 minutes on the app weekly over the study, with most of the time spent on the SnackApp dashboard.
What next?
The SnackApp will be refined to improve its functions and useability and then used in further randomised control trials to test its usefulness in promoting participation in Snacktivity™.
Citation details
Sanders JP, Gokal K, Thomas JJC, Rawstorn JC, Sherar LB, Maddison R, Greaves CJ, Esliger D, Daley AJ and Snacktivity Investigators. Development of a Mobile Health Snacktivity App to Promote Physical Activity in Inactive Adults (SnackApp): Intervention Mapping and User Testing Study. JMIR Formative Research. 2023. DOI: 10.2196/41114
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Birmingham Community Health care Foundation National Health Service Trust, the Clinical Research Network, West Midlands, and the general practices who supported the study. The authors would like to thank all those who participated in this research. This project was funded as part of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) under its Program Grants for Applied Research (RP-PG-0618-20008). This research was supported by the NIHR Leicester Biomedical Research Centre. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the National Health Service, NIHR, or Department of Health and Social Care.
Our researchers


