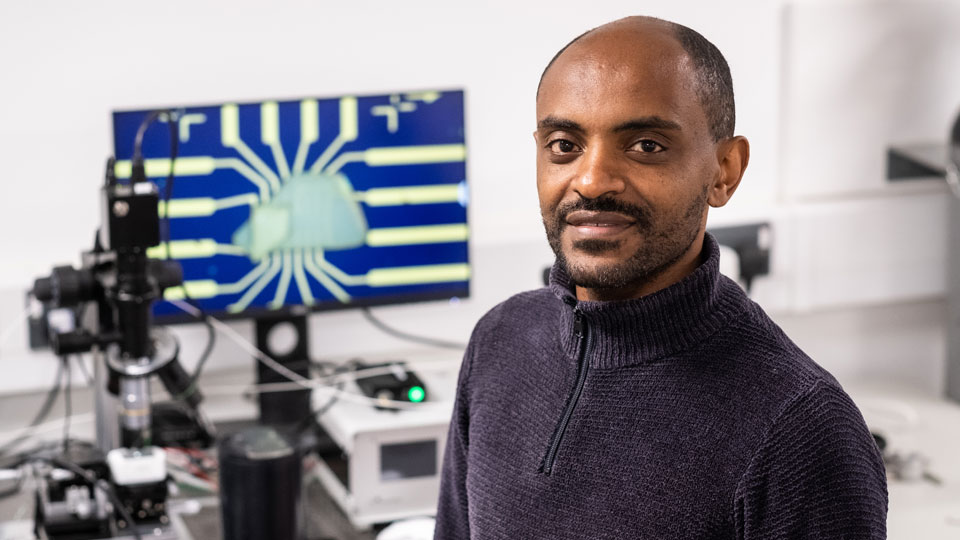
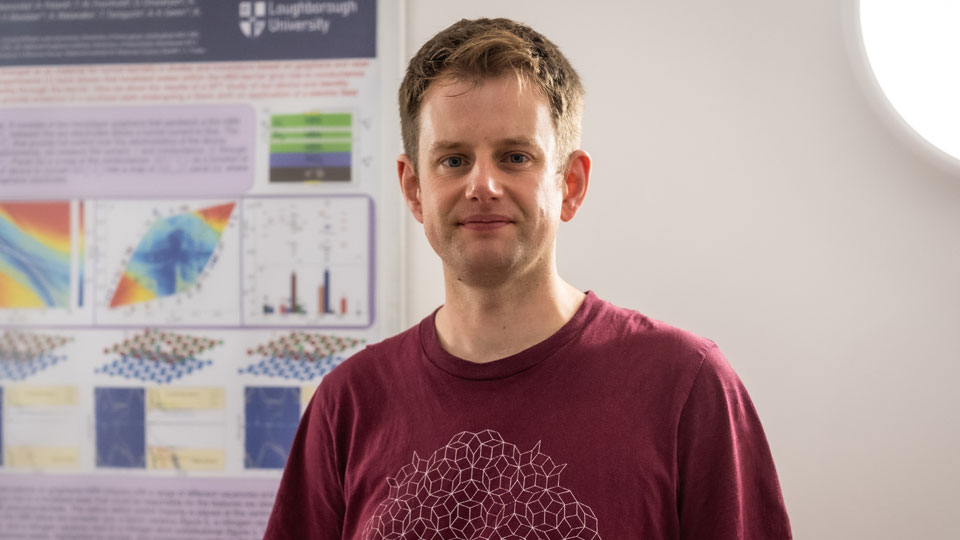
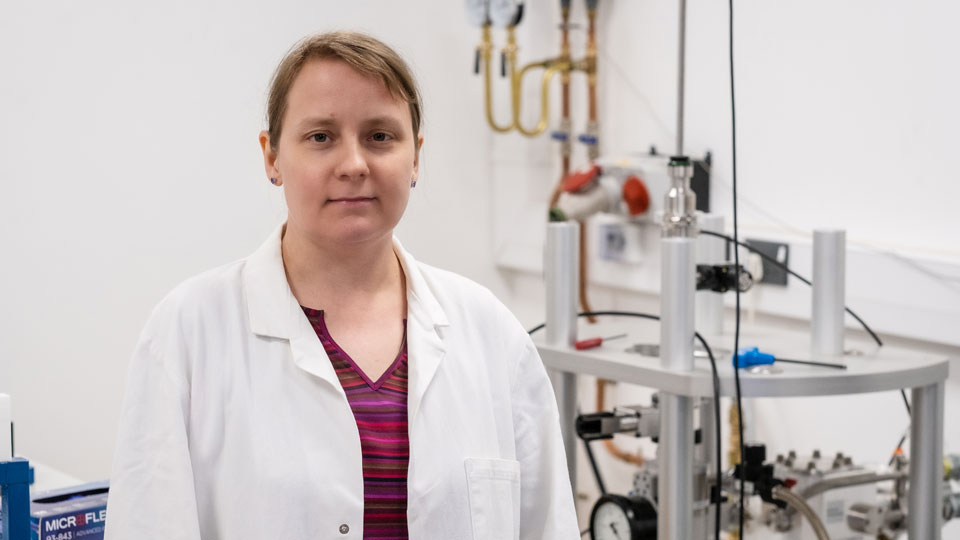
Twistronics (moiré)
Moiré typically refers to the visual of a pattern overlaid on top of another pattern that is similar, but not exactly the same.
Moiré patterns are a type of interference pattern and, like the golden ratio, originate in mathematics and physics.
Feather image (below) courtesy of fir0002 flagstaffotos@gmail.com
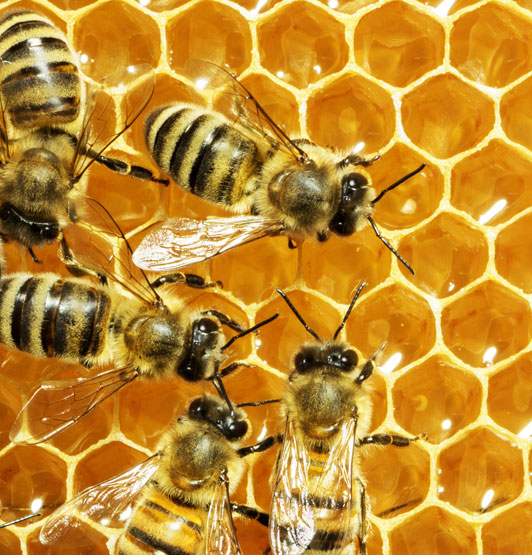

Nature’s engineers
From birth, honey bees know how to build perfect patterns, and construct their hives as a hexagonal lattice of holes which start as cylinders. It is thought that the ‘construction behaviour’ of bees results in the hexagonal arrangement - which is a stroke of lucky as it's the most efficient use of space! This hexagonal lattice is similar to what we see in graphene - defined as a single atomic layer created from graphite. Graphene was one of the first two dimensional (2D) materials reported and was awarded a Nobel Prize in 2010.
How can the moiré effect be used?
Future applications of the moiré effect include:
- Magnetic memory vices
- Artificial intelligence building blocks
- Non-invasive medical diagnosis
- Solar and thermal energy
- Energy storage
- Perfect optical surfaces
Related research at Loughborough
There are a variety of research areas that benefit from greater understanding or use of moiré effects.


