Abstract
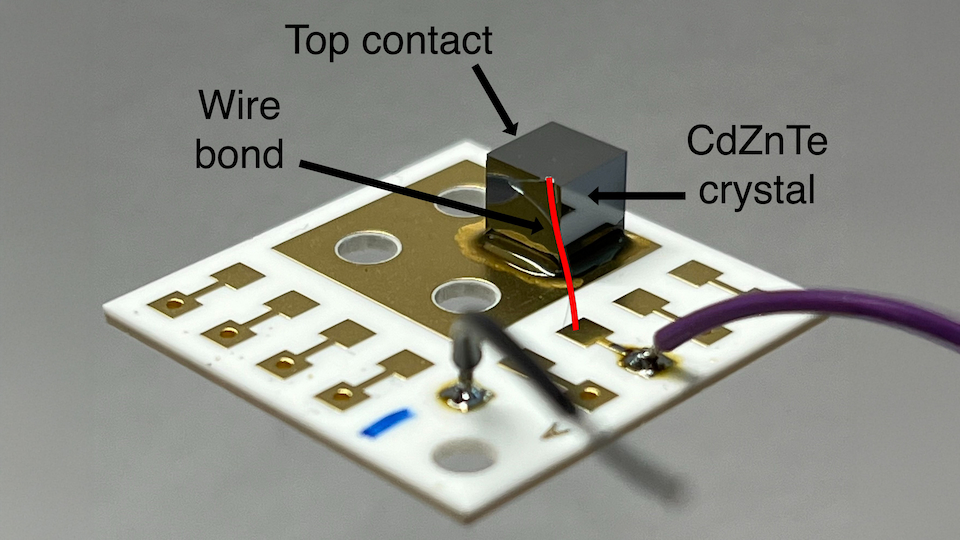
CdZnTe is widely used in gamma ray radiation detection for medical imaging and security, with growing interest in CdZnTe for synchrotron and XFEL detector materials at X-ray fluxes in excess of 1010 photons·s-1mm-2. Understanding fundamental material properties allows for greater understanding of the relevancy of CdZnTe for use at photon light sources. This investigation uses alpha particle spectroscopy to directly compare the mobility-lifetime products (μτ) and mobilities (μ) of High-Flux (HF) and Low-Flux (LF) CdZnTe, produced by Redlen Technologies, and ascertain the differences in bulk charge carrier properties for both electrons and holes. This work presents average values of HF-CdZnTe to be μe = 920 cm V-1 s-1, μh = 38 cm V-1 s-1, μeτe = 4.4 × 10-3 cm V-1 s-1, μhτh = 1.6 × 10-4 cm V-1 s-1 and LF-CdZnTe with μe = 840 cm V-1 s-1, μeτe = 12 × 10-3 cm V-1 s-1, μhτh = 0.4 × 10-4 cm V-1 s-1.