Therapeutics & Diagnostics
Rapid point-of-care sensor for pneumonia diagnosis in hospital, community and home settings
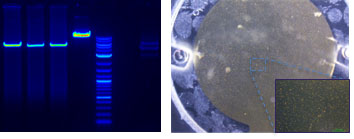 (Left) DNA detection in agarose gel electrophoresis; (Right) Quartz crystal microbalance coupled with fluidic system for sample delivery. Section shows protein-coated microbeads immobilised on to the sensor surface.
(Left) DNA detection in agarose gel electrophoresis; (Right) Quartz crystal microbalance coupled with fluidic system for sample delivery. Section shows protein-coated microbeads immobilised on to the sensor surface.UK’s AMR strategy recognises the need for quicker diagnosis to allow targeted treatment and restricted use of valuable broad-spectrum antibiotics, thus controlling antibiotic resistance. This project is employing novel nonlinear acoustic technology coupled with air-borne bio-particle capture technology to develop a novel pneumonia test from biomarkers in breath that can distinguish it from flu potentially in a few minutes. The project involves novel advancements in the design of instrumentation and of biomolecular recognition elements (aptamers) to allow sensitive and specific detection of the biomarkers potentially allowing multiplexing capability on a single sensor chip for the first time.
Staff: S Ghosh
